Biogas :
Biogas :
Biogas has emerged as a promising alternative energy source with significant environmental and economic benefits. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of biogas, from its production to its applications and future prospects.
Biogas has emerged as a promising alternative energy source with significant environmental and economic benefits. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of biogas, from its production to its applications and future prospects.
Introduction to Biogas
Introduction to Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. It is a versatile fuel that can be utilized for various purposes, ranging from electricity generation to cooking and heating.
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. It is a versatile fuel that can be utilized for various purposes, ranging from electricity generation to cooking and heating.
What is Biogas?
What is Biogas?
Definition
Biogas is a mixture of gases primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), along with traces of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitrogen (N2).
Composition
The composition of biogas typically varies depending on the feedstock used in the anaerobic digestion process. However, methane content generally ranges from 50% to 70%, making it a valuable energy source.
Definition
Biogas is a mixture of gases primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), along with traces of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitrogen (N2).
Composition
The composition of biogas typically varies depending on the feedstock used in the anaerobic digestion process. However, methane content generally ranges from 50% to 70%, making it a valuable energy source.






How is Biogas Produced?
How is Biogas Produced?
Anaerobic Digestion Process
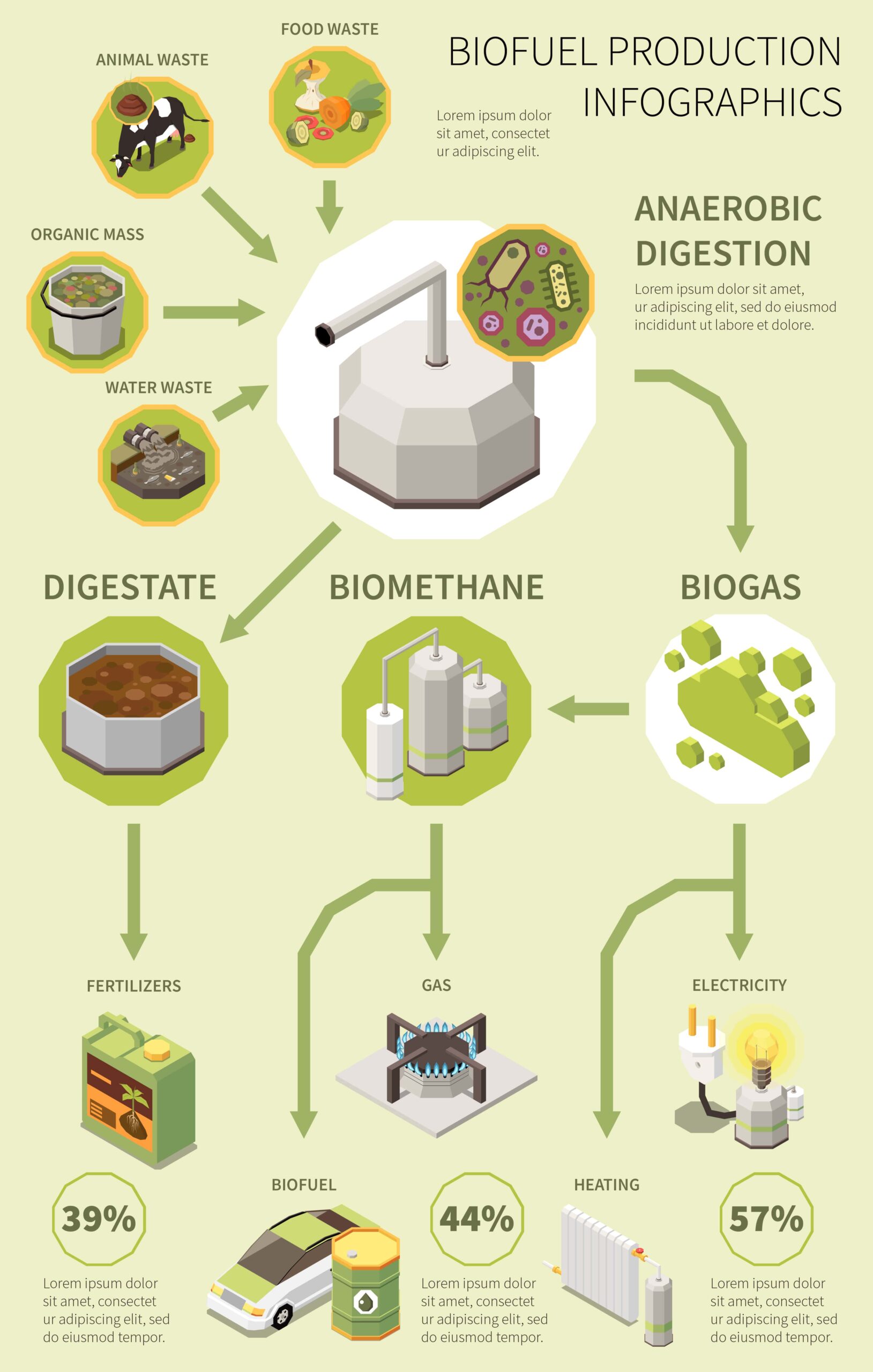
Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, animal manure, sewage sludge, and food waste. This process involves the breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the release of methane gas.
Types of Feedstock
Various organic materials can serve as feedstock for biogas production, including:
- Crop residues
- Livestock manure
- Organic waste from households and industries
Anaerobic Digestion Process
Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, animal manure, sewage sludge, and food waste. This process involves the breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the release of methane gas.
Types of Feedstock
Various organic materials can serve as feedstock for biogas production, including:
- Crop residues
- Livestock manure
- Organic waste from households and industries





Benefits of Biogas
Benefits of Biogas
Environmental Impact
Biogas production helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and converting it into a usable energy source. Additionally, it reduces reliance on fossil fuels, thereby contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Energy Production
Biogas can be used to generate electricity and heat, providing a renewable and sustainable energy source for both residential and industrial applications. It offers a reliable alternative to conventional fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
Waste Management
Biogas production facilitates the proper management and treatment of organic waste, thereby reducing environmental pollution and odors associated with decomposing organic matter. It promotes the efficient utilization of waste materials for energy generation.
Environmental Impact
Biogas production helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and converting it into a usable energy source. Additionally, it reduces reliance on fossil fuels, thereby contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Energy Production
Biogas can be used to generate electricity and heat, providing a renewable and sustainable energy source for both residential and industrial applications. It offers a reliable alternative to conventional fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
Waste Management
Biogas production facilitates the proper management and treatment of organic waste, thereby reducing environmental pollution and odors associated with decomposing organic matter. It promotes the efficient utilization of waste materials for energy generation.
Applications of Biogas
Applications of Biogas
Electricity Generation
Biogas can be combusted in engines or turbines to generate electricity, either for on-site use or grid injection. This decentralized energy production approach offers resilience and flexibility, particularly in rural areas with limited access to centralized power grids.
Heating and Cooking
Biogas can be utilized for heating purposes in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. It can also replace traditional cooking fuels such as wood, charcoal, or LPG, providing a cleaner and more sustainable cooking solution.
Transportation Fuel
Biogas can be upgraded to biomethane, a renewable natural gas suitable for use as a transportation fuel in compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles. Biomethane offers lower emissions compared to conventional fuels, contributing to cleaner air quality and reduced carbon footprint.
Electricity Generation
Biogas can be combusted in engines or turbines to generate electricity, either for on-site use or grid injection. This decentralized energy production approach offers resilience and flexibility, particularly in rural areas with limited access to centralized power grids.
Heating and Cooking
Biogas can be utilized for heating purposes in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. It can also replace traditional cooking fuels such as wood, charcoal, or LPG, providing a cleaner and more sustainable cooking solution.
Transportation Fuel
Biogas can be upgraded to biomethane, a renewable natural gas suitable for use as a transportation fuel in compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles. Biomethane offers lower emissions compared to conventional fuels, contributing to cleaner air quality and reduced carbon footprint.
Challenges and Limitations
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous benefits, biogas production faces several challenges and limitations, including:
Feedstock Availability
The availability and quality of feedstock can significantly impact biogas production efficiency. Factors such as seasonal variations, transportation costs, and competition for feedstock can pose challenges to biogas plant operations.
Technical Challenges
Biogas production technologies require proper design, operation, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Technical challenges such as process instability, gas quality issues, and equipment breakdowns can hinder biogas production.
Economic Viability
The economic viability of biogas projects depends on factors such as capital investment, operating costs, energy prices, and government incentives. Financial barriers and market uncertainties can affect the profitability and sustainability of biogas ventures.
Despite its numerous benefits, biogas production faces several challenges and limitations, including:
Feedstock Availability
The availability and quality of feedstock can significantly impact biogas production efficiency. Factors such as seasonal variations, transportation costs, and competition for feedstock can pose challenges to biogas plant operations.
Technical Challenges
Biogas production technologies require proper design, operation, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Technical challenges such as process instability, gas quality issues, and equipment breakdowns can hinder biogas production.
Economic Viability
The economic viability of biogas projects depends on factors such as capital investment, operating costs, energy prices, and government incentives. Financial barriers and market uncertainties can affect the profitability and sustainability of biogas ventures.
Future Prospects of Biogas
Future Prospects of Biogas
Despite the challenges, biogas holds significant potential as a renewable energy source with the following future prospects:
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve biogas production technologies, enhance process efficiency, and expand the range of feedstock options. Innovations such as advanced anaerobic digestion systems, biogas upgrading technologies, and co-digestion strategies can further optimize biogas production.
Policy Support
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting biogas development and deployment. Supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs, renewable energy mandates, tax incentives, and grants can stimulate investment in biogas projects and create a favorable regulatory environment.
Despite the challenges, biogas holds significant potential as a renewable energy source with the following future prospects:
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve biogas production technologies, enhance process efficiency, and expand the range of feedstock options. Innovations such as advanced anaerobic digestion systems, biogas upgrading technologies, and co-digestion strategies can further optimize biogas production.
Policy Support
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting biogas development and deployment. Supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs, renewable energy mandates, tax incentives, and grants can stimulate investment in biogas projects and create a favorable regulatory environment.
Conclusion
Conclusion
In conclusion, biogas offers a sustainable solution to the dual challenges of waste management and energy production. With its environmental benefits, diverse applications, and ongoing technological advancements, biogas has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
In conclusion, biogas offers a sustainable solution to the dual challenges of waste management and energy production. With its environmental benefits, diverse applications, and ongoing technological advancements, biogas has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Unique FAQs
Unique FAQs
Is biogas production suitable for all types of organic waste?
Ans: Biogas production can utilize various organic materials, but not all waste streams are equally suitable. Factors such as moisture content, nutrient composition, and biodegradability influence the feasibility of biogas production from specific feedstock.
What are the environmental benefits of biogas?
Ans: Biogas production helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, reduces dependence on fossil fuels, and promotes sustainable waste management practices. It contributes to climate change mitigation, improves air quality, and reduces environmental pollution.
Can biogas be stored for future use?
Ans: Biogas can be stored in tanks or pipelines for future use, either in its raw form or after upgrading to biomethane. Storage options include compression or liquefaction for transportation fuel applications, as well as buffer storage for electricity generation and heating.
What are the challenges associated with biogas production?
Ans: Challenges such as feedstock availability, technical complexity, and economic viability can affect biogas production. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach involving technological innovation, policy support, and stakeholder engagement.
How does biogas compare to other renewable energy sources?
Ans: Biogas offers unique advantages such as decentralized production, waste management benefits, and versatility in applications. Compared to other renewables like solar and wind, biogas provides a reliable and dispatchable energy source with continuous availability, complementing intermittent sources.
What is the lifespan of a biogas plant?
Ans: The lifespan of a biogas plant can vary depending on factors such as design, construction quality, and maintenance practices. Generally, well-maintained biogas plants can operate efficiently for 15 to 20 years or more.
Is biogas production economically viable for small-scale applications? Biogas production can be economically viable for small-scale applications such as household digesters or community-based systems. However, economic feasibility depends on factors such as feedstock availability, energy prices, and upfront investment costs.
Does biogas production require specialized knowledge or skills?
Ans: While biogas production involves technical processes, it does not necessarily require specialized knowledge or skills. Basic understanding of anaerobic digestion principles, safety procedures, and maintenance practices can enable individuals or communities to operate biogas plants effectively.
Can biogas production contribute to rural development?
Ans: Biogas production has the potential to contribute to rural development by providing access to clean energy, improving waste management practices, and creating job opportunities. Biogas projects can enhance agricultural productivity, support local economies, and improve living standards in rural areas.
What role does government policy play in promoting biogas adoption? Ans: Government policy plays a crucial role in promoting biogas adoption through incentives, subsidies, regulations, and supportive frameworks. Policies such as renewable energy targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, and financial incentives can encourage investment in biogas projects and facilitate market growth.
Is biogas production suitable for all types of organic waste?
Ans: Biogas production can utilize various organic materials, but not all waste streams are equally suitable. Factors such as moisture content, nutrient composition, and biodegradability influence the feasibility of biogas production from specific feedstock.
What are the environmental benefits of biogas?
Ans: Biogas production helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, reduces dependence on fossil fuels, and promotes sustainable waste management practices. It contributes to climate change mitigation, improves air quality, and reduces environmental pollution.
Can biogas be stored for future use?
Ans: Biogas can be stored in tanks or pipelines for future use, either in its raw form or after upgrading to biomethane. Storage options include compression or liquefaction for transportation fuel applications, as well as buffer storage for electricity generation and heating.
What are the challenges associated with biogas production?
Ans: Challenges such as feedstock availability, technical complexity, and economic viability can affect biogas production. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach involving technological innovation, policy support, and stakeholder engagement.
How does biogas compare to other renewable energy sources?
Ans: Biogas offers unique advantages such as decentralized production, waste management benefits, and versatility in applications. Compared to other renewables like solar and wind, biogas provides a reliable and dispatchable energy source with continuous availability, complementing intermittent sources.
What is the lifespan of a biogas plant?
Ans: The lifespan of a biogas plant can vary depending on factors such as design, construction quality, and maintenance practices. Generally, well-maintained biogas plants can operate efficiently for 15 to 20 years or more.
Is biogas production economically viable for small-scale applications? Biogas production can be economically viable for small-scale applications such as household digesters or community-based systems. However, economic feasibility depends on factors such as feedstock availability, energy prices, and upfront investment costs.
Does biogas production require specialized knowledge or skills?
Ans: While biogas production involves technical processes, it does not necessarily require specialized knowledge or skills. Basic understanding of anaerobic digestion principles, safety procedures, and maintenance practices can enable individuals or communities to operate biogas plants effectively.
Can biogas production contribute to rural development?
Ans: Biogas production has the potential to contribute to rural development by providing access to clean energy, improving waste management practices, and creating job opportunities. Biogas projects can enhance agricultural productivity, support local economies, and improve living standards in rural areas.
What role does government policy play in promoting biogas adoption? Ans: Government policy plays a crucial role in promoting biogas adoption through incentives, subsidies, regulations, and supportive frameworks. Policies such as renewable energy targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, and financial incentives can encourage investment in biogas projects and facilitate market growth.


I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I don’t know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
One thing I would like to comment on is that fat burning plan fast may be possible by the right diet and exercise. Your size not just affects the look, but also the general quality of life. Self-esteem, depressive disorders, health risks, along with physical ability are influenced in an increase in weight. It is possible to do everything right and at the same time having a gain. Should this happen, a problem may be the offender. While an excessive amount food and never enough workout are usually responsible, common health concerns and traditionally used prescriptions may greatly help to increase size. Thanks for your post in this article.
An added important part is that if you are a senior citizen, travel insurance intended for pensioners is something you ought to really take into account. The more aged you are, greater at risk you happen to be for allowing something poor happen to you while in foreign countries. If you are never covered by a number of comprehensive insurance, you could have quite a few serious issues. Thanks for discussing your guidelines on this blog site.
It抯 onerous to search out educated folks on this topic, but you sound like you know what you抮e speaking about! Thanks
Thanks for revealing your ideas on this blog. Furthermore, a misconception regarding the banks intentions if talking about property foreclosure is that the loan company will not take my repayments. There is a degree of time the bank can take payments occasionally. If you are too deep within the hole, they’re going to commonly desire that you pay the particular payment in whole. However, i am not saying that they will have any sort of payments at all. When you and the loan company can seem to work a thing out, the actual foreclosure approach may stop. However, if you continue to skip payments in the new strategy, the foreclosures process can just pick up from where it left off.
fantastic publish, very informative. I wonder why the opposite experts of this sector do not understand this. You must continue your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!